How To Improve Wrist Stability And Prevent Injuries During Weightlifting Or Repetitive Motions?
Strong and stable wrists are important in everyday life. We often take our wrists for granted, but they are involved in almost every activity we do. The muscles, tendons, and ligaments in the wrist work together to allow us to perform a wide range of movements, such as gripping, turning, pushing, and pulling.
Wrist stability is essential for optimal function and to prevent injury. When the wrist is unstable, it can cause pain, weakness, and a decreased ability to perform daily activities. In this article, we will explore how wrist stability works and share some tips and FAQs to improve wrist health and function.
Details About Wrist Stability
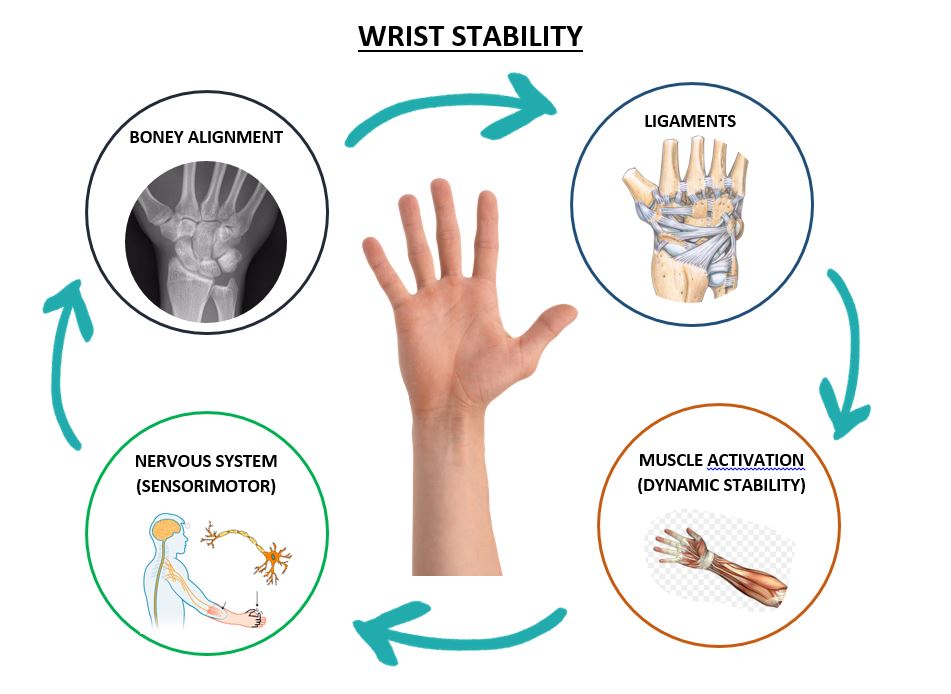
Wrist stability involves the proper alignment and function of the bones, tendons, and ligaments in the wrist. The wrist joint is made up of the radius and ulna bones of the forearm, eight small carpal bones in the wrist, and the hand bones.
The bones in the wrist are held together by ligaments and tendons that provide support and stability. The tendons connect the muscles in the forearm to the wrist bones and help to move the wrist joint. Ligaments are strong, fibrous bands that connect bone to bone and provide stability to the joint.
The muscles in the wrist work together to control and stabilize the joint. The wrist flexors are located on the palm side of the forearm and control wrist flexion (bending the wrist towards the palm). The wrist extensors are located on the back of the forearm and control wrist extension (bending the wrist backwards).
In addition to the muscles, there are several small joints in the wrist that provide stability. These joints are called intercarpal joints and are responsible for the precise movements of the wrist.
Tips for Wrist Stability
There are several tips to improve wrist stability and function:
- Stretch regularly- Stretching can prevent tightness and improve range of motion in the wrist. Try wrist flexion and extension stretches by holding your arm out straight and bending your wrist up and down. Hold for 10-15 seconds and repeat 2-3 times per day.
- Strengthen the muscles- Strengthening exercises can improve stability and prevent injury. Wrist curls and reverse wrist curls help to strengthen the wrist flexors and extensors respectively. Use 1-2lb weights and perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 reps, 2-3 times per week.
- Maintain proper posture- Poor posture can place additional stress on the wrist and cause instability. Keep your wrists straight and in line with your forearms when typing or using a computer.
- Use proper technique during sports- Sports such as tennis, golf, and weightlifting require repetitive wrist movements. Use proper technique and avoid overuse to prevent wrist injury.
- Avoid repetitive stress- Repetitive stress and overuse can cause wrist pain and instability. Take frequent breaks and stretch regularly to prevent injury.
- Wear supportive braces- Wrist braces can provide support and stability to the joint, especially during activities that require repetitive wrist movements.
- Use ergonomic equipment- Ergonomic keyboards and mice can reduce stress on the wrist and prevent injury.
- Stay hydrated- Proper hydration helps to keep the tendons and ligaments in the wrist healthy and flexible.
FAQs About Wrist Stability
What causes wrist instability?
Wrist instability can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, overuse, poor posture, and repetitive wrist movements.
What are the symptoms of wrist instability?
The symptoms of wrist instability may include pain, swelling, weakness, and a decreased ability to perform daily activities.
Can wrist instability be prevented?
Yes, wrist instability can be prevented by stretching regularly, strengthening the muscles, maintaining proper posture, wearing supportive braces, avoiding repetitive stress, and using ergonomic equipment.
How is wrist instability treated?
Treatment for wrist instability may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation, as well as physical therapy and bracing. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
When should I see a doctor for wrist instability?
You should see a doctor if you experience persistent pain, swelling, or weakness in your wrist, or if your symptoms do not improve with home remedies.
Are there any exercises I should avoid if I have wrist instability?
If you have wrist instability, you should avoid exercises that involve repetitive wrist movements or place stress on the joint, such as push-ups, dips, or forearm curls.
Can I still exercise with wrist instability?
Yes, you can still exercise with wrist instability, but you should modify or avoid exercises that aggravate your symptoms. Consult with your doctor or physical therapist for individualized recommendations.
In conclusion, wrist stability is essential for optimal function and to prevent injury. By following the tips and FAQs outlined in this article, you can improve wrist health and function. Remember to stretch regularly, strengthen the muscles, maintain proper posture, and avoid repetitive stress to keep your wrists strong and stable.



Post a Comment for "How To Improve Wrist Stability And Prevent Injuries During Weightlifting Or Repetitive Motions?"